Tableau and Looker are both powerful Business Intelligence (BI) tools, but they have different strengths and capabilities. The choice between Tableau and Looker depends on your specific business needs and preferences. Below, I’ll provide an overview of each tool and highlight some considerations to help you decide which one is best for you.
Tableau
1. Data Visualization: Tableau is known for its robust data visualization capabilities. It offers a wide range of chart types and interactive features to create compelling visualizations.
2. User-Friendly: Tableau is user-friendly and often preferred by business users. It has a drag-and-drop interface that makes it easy to create dashboards and reports.
3. Integration: Tableau integrates well with various data sources, including databases, cloud storage, and web services. It has a strong ecosystem of connectors.
4. Performance: Tableau is known for its performance and speed in rendering visualizations, especially with large datasets.
5. Desktop and Web: Tableau offers both desktop and web-based versions, making it flexible for different types of users and use cases.
Example
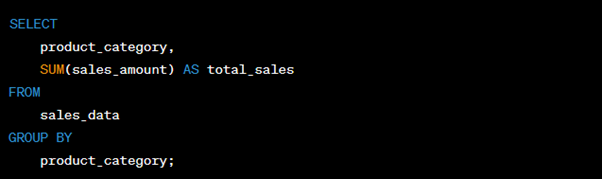
Here’s a basic example of a Tableau visualization code that creates a bar chart showing sales by product category:
Looker
1. Data Modeling: Looker focuses on data modeling and offers a semantic layer that abstracts complex SQL queries. It allows business users to explore data with less reliance on SQL knowledge.
2. Data Governance: Looker provides strong data governance features, including central data modeling and security settings.
3. Customization: Looker allows for extensive customization and embedding of dashboards and reports within other applications.
4. Collaboration: Looker emphasizes collaboration through shared “Looks” (saved queries) and interactive dashboards.
5. Version Control: Looker includes version control for modeling, which is valuable for managing changes in complex data models.
Example
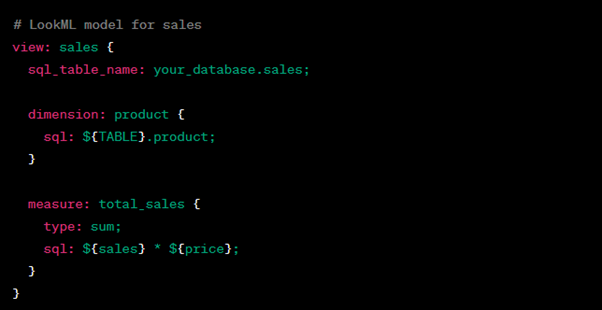
In Looker, you define data models using LookML, a modeling language. Here’s an example of LookML code for a sales model:
Considerations
1. User Skillset: Consider the technical proficiency of your team. Tableau may be preferred by those who are comfortable with visual data exploration, while Looker may be better for teams with strong SQL and data modeling skills.
2. Data Complexity: If your data is highly complex and requires extensive modeling, Looker’s data modeling capabilities may be advantageous.
3. Scalability: Consider the scalability of your BI needs. Tableau is known for its performance with large datasets, while Looker’s central data modeling can simplify scaling.
4. Customization: Looker offers more customization options, making it suitable for organizations with specific branding and embedding requirements.
5. Cost: Compare the pricing structures of both tools, including licensing, user fees, and any additional costs for data connectors or features.
Ultimately, the choice between Tableau and Looker depends on your organization’s specific requirements, user skills, and budget constraints. It’s advisable to conduct a thorough evaluation and, if possible, try both tools with your data to determine which one aligns best with your BI goals.
